Abstract
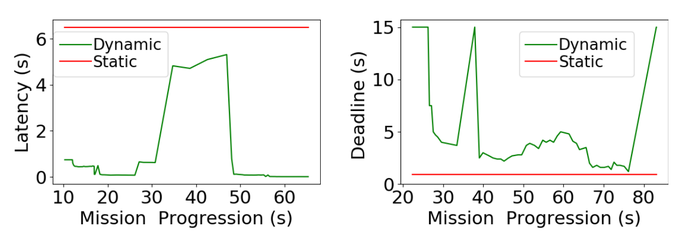
The limited onboard energy of autonomous mobile robots poses a tremendous challenge for practical deployment. Hence, efficient computing solutions are imperative. A crucial shortcoming of state-of-the-art computing solutions is that they ignore the robot’s operating environment heterogeneity and make static, worst-case assumptions. As this heterogeneity impacts the system’s computing payload, an optimal system must dynamically capture these changes in the environment and adjust its computational resources accordingly. This paper introduces RoboRun, a mobile-robot runtime that dynamically exploits the compute-environment synergy to improve performance and energy. We implement RoboRun in the Robot Operating System (ROS) and evaluate it on autonomous drones. We compare RoboRun against a state-of-the-art static design and show 4.5X and 4X improvements in mission time and energy, respectively, as well as a 36% reduction in CPU utilization.